Authors: Dewu Zheng, Yanlin Wang, Ensheng Shi, Hongyu Zhang, Zibin Zheng
Abstract: Recently, an increasing number of AI-driven programming assistants powered by
code LLMs have been integrated into various real-world software development
environments, significantly boosting developer productivity. However, existing
code generation benchmarks primarily focus on general-purpose scenarios,
leaving the code generation performance of LLMs for specific application
domains largely unknown. In this paper, we introduce a new benchmark,
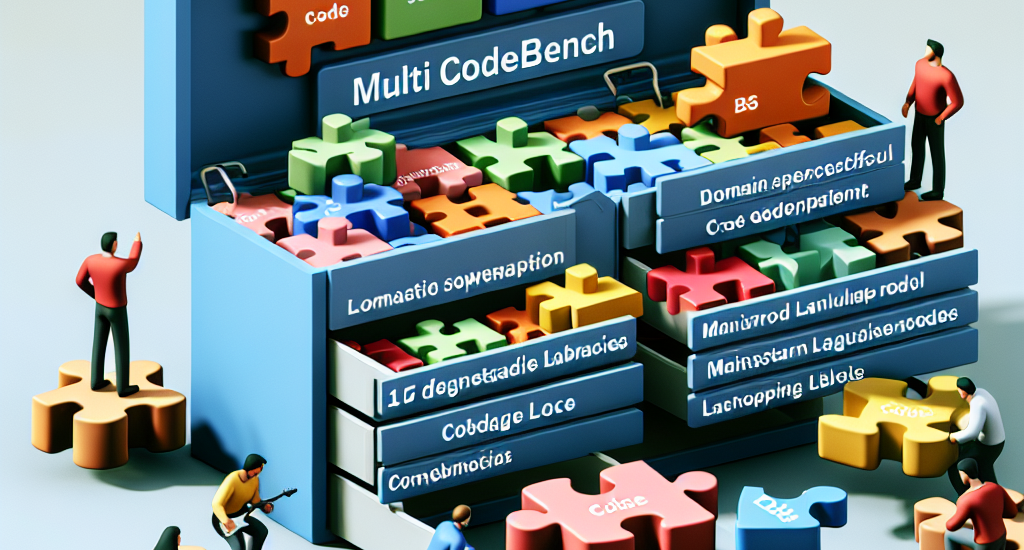
MultiCodeBench, to fill this gap. MultiCodeBench comprises 2,400 programming
tasks, covering 12 popular software development domains and 15 programming
languages. Specifically, we perform in-depth research to identify these 12
application domains. Given that each domain may involve multiple technical
frameworks, and that different frameworks present distinct challenges in the
coding process, we categorize the commonly used frameworks and platforms within
each domain. We then sample programming problems from GitHub repositories
related to these subdomains. To ensure the quality of the tasks and mitigate
data leakage issues, we invite annotators to rewrite the docstrings for each
task in MultiCodeBench. Additionally, we build a static analysis-based
dependency parsing tool to extract the dependencies in the ground truth for
each task, enabling deeper performance analysis. Through extensive experiments
on MultiCodeBench with eleven representative mainstream LLMs, we reveal the
code generation performance of the LLMs across different application domains,
providing practical insights for developers in downstream fields when selecting
LLMs. Furthermore, we analyze the reasons behind the models’ failures in
completing software application development tasks, offering guidance for model
developers to enhance domain-specific code generation capabilities.
Source: http://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18573v1