Authors: Haoyu Dong, Hanxue Gu, Yaqian Chen, Jichen Yang, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Abstract: Segment Anything Model (SAM) has gained significant attention because of its
ability to segment a variety of objects in images given a prompt. The recently
developed SAM 2 has extended this ability to video inputs. This opens an
opportunity to apply SAM to 3D images, one of the fundamental tasks in the
medical imaging field. In this paper, we provide an extensive evaluation of SAM
2’s ability to segment both 2D and 3D medical images. We collect 18 medical
imaging datasets, including common 3D modalities such as computed tomography
(CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET)
as well as 2D modalities such as X-ray and ultrasound. We consider two
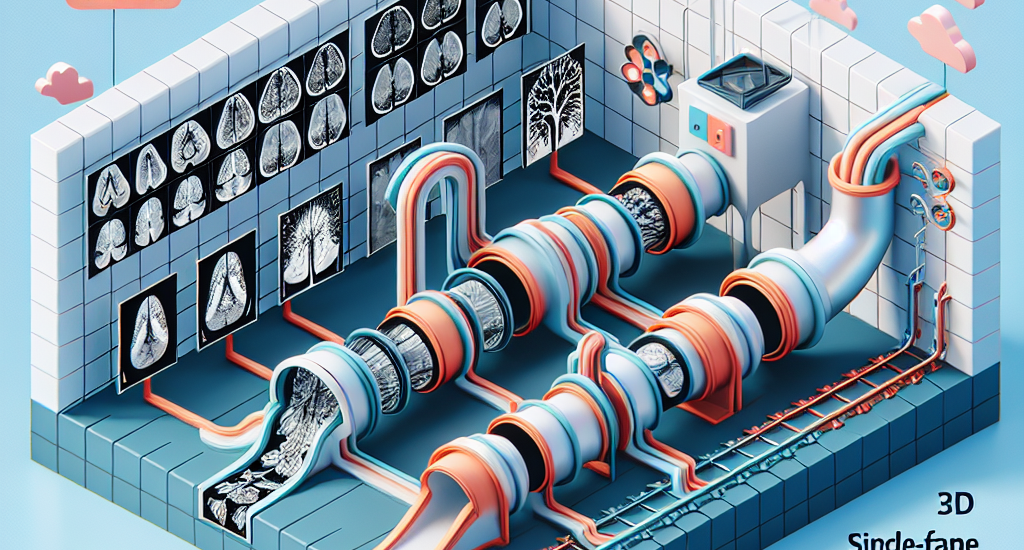
evaluation pipelines of SAM 2: (1) multi-frame 3D segmentation, where prompts
are provided to one or multiple slice(s) selected from the volume, and (2)
single-frame 2D segmentation, where prompts are provided to each slice. The
former is only applicable to 3D modalities, while the latter applies to both 2D
and 3D modalities. We learn that SAM 2 exhibits similar performance as SAM
under single-frame 2D segmentation, and has variable performance under
multi-frame 3D segmentation depending on the choices of slices to annotate, the
direction of the propagation, the predictions utilized during the propagation,
etc.
Source: http://arxiv.org/abs/2408.00756v1