Authors: Liana Mikaelyan, Ayyoob Imani, Mathew Salvaris, Parth Pathak, Mohsen Fayyaz
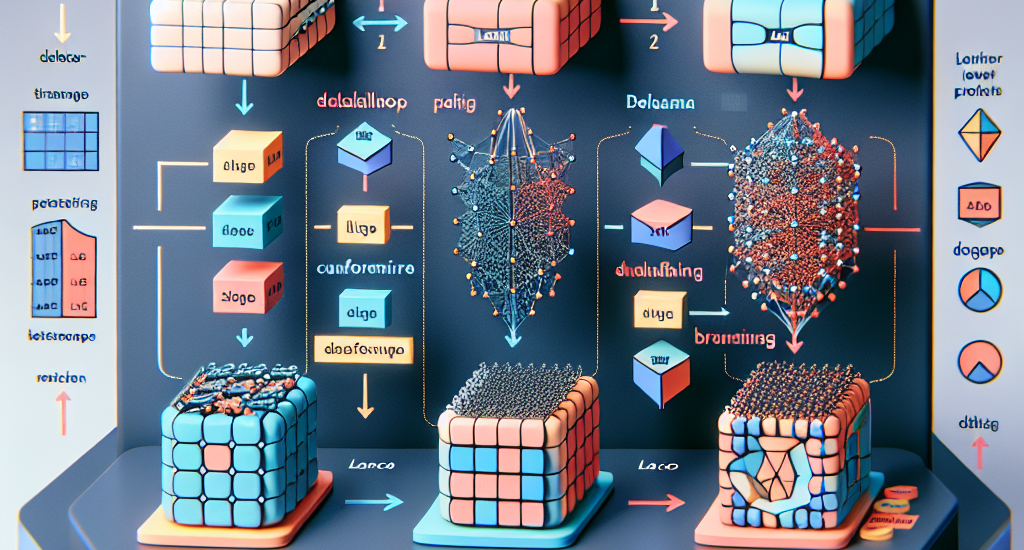
Abstract: We introduce DeltaLLM, a new post-training compression technique to reduce
the memory footprint of LLMs. We propose an alternative way of structuring LLMs
with weight sharing between layers in subsequent Transformer blocks, along with
additional low-rank difference matrices between them. For training, we adopt
the progressing module replacement method and show that the lightweight
training of the low-rank modules with approximately 30M-40M tokens is
sufficient to achieve performance on par with LLMs of comparable sizes trained
from scratch. We release the resultant models, DeltaLLAMA and DeltaPHI, with a
12% parameter reduction, retaining 90% of the performance of the base Llama and
Phi models on common knowledge and reasoning benchmarks. Our method also
outperforms compression techniques JointDrop, LaCo, ShortGPT and SliceGPT with
the same number of parameters removed. For example, DeltaPhi 2.9B with a 24%
reduction achieves similar average zero-shot accuracies as recovery fine-tuned
SlicedPhi 3.3B with a 12% reduction, despite being approximately 400M
parameters smaller with no fine-tuning applied. This work provides new insights
into LLM architecture design and compression methods when storage space is
critical.
Source: http://arxiv.org/abs/2501.18596v1