Authors: Senqiao Yang, Yukang Chen, Zhuotao Tian, Chengyao Wang, Jingyao Li, Bei Yu, Jiaya Jia
Abstract: Recent advancements in vision-language models have enhanced performance by
increasing the length of visual tokens, making them much longer than text
tokens and significantly raising computational costs. However, we observe that
the visual tokens generated by popular vision encoders, such as CLIP and
SigLIP, contain significant redundancy. To address this, we introduce
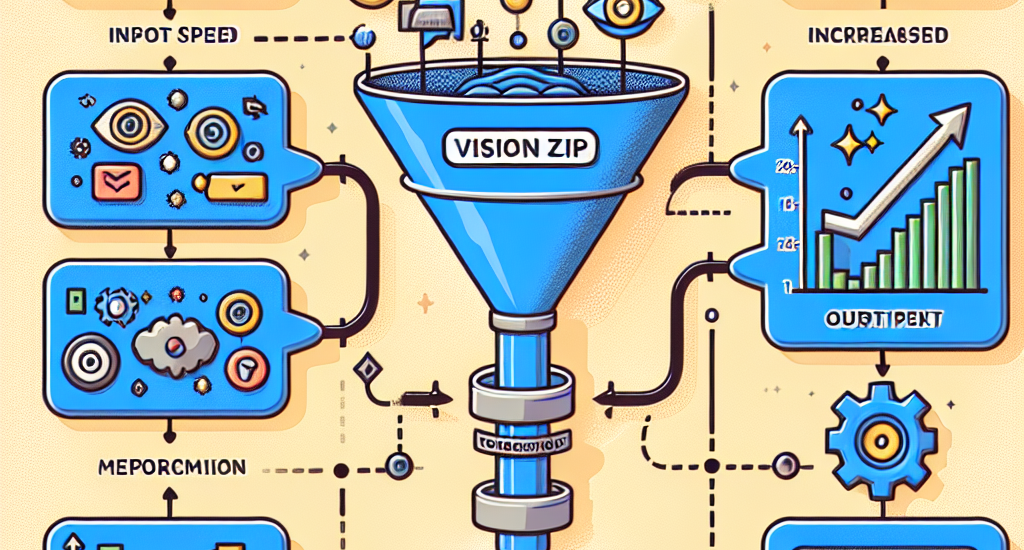
VisionZip, a simple yet effective method that selects a set of informative
tokens for input to the language model, reducing visual token redundancy and
improving efficiency while maintaining model performance. The proposed
VisionZip can be widely applied to image and video understanding tasks and is
well-suited for multi-turn dialogues in real-world scenarios, where previous
methods tend to underperform. Experimental results show that VisionZip
outperforms the previous state-of-the-art method by at least 5% performance
gains across nearly all settings. Moreover, our method significantly enhances
model inference speed, improving the prefilling time by 8x and enabling the
LLaVA-Next 13B model to infer faster than the LLaVA-Next 7B model while
achieving better results. Furthermore, we analyze the causes of this redundancy
and encourage the community to focus on extracting better visual features
rather than merely increasing token length. Our code is available at
https://github.com/dvlab-research/VisionZip .
Source: http://arxiv.org/abs/2412.04467v1