Authors: Seongmin Lee, Hsiang Hsu, Chun-Fu Chen
Abstract: LLM hallucination, where LLMs occasionally generate unfaithful text, poses
significant challenges for their practical applications. Most existing
detection methods rely on external knowledge, LLM fine-tuning, or
hallucination-labeled datasets, and they do not distinguish between different
types of hallucinations, which are crucial for improving detection performance.
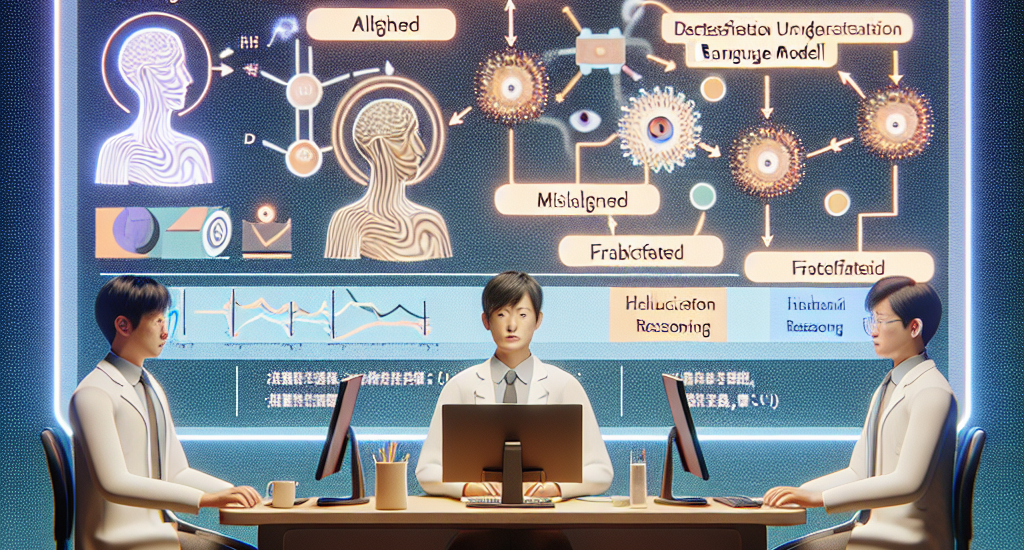
We introduce a new task, Hallucination Reasoning, which classifies
LLM-generated text into one of three categories: aligned, misaligned, and
fabricated. Our novel zero-shot method assesses whether LLM has enough
knowledge about a given prompt and text. Our experiments conducted on new
datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in hallucination reasoning
and underscore its importance for enhancing detection performance.
Source: http://arxiv.org/abs/2411.09689v1